Tech
Detecting ChatGPT Plagiarism – And Why It’s So Difficult To Do?

(CTN NEWS) – ChatGPT is one of the most popular chatbots available today. However, because of how potent and humanlike its responses are, academics, teachers, and editors all have to deal with increased plagiarism and cheating caused by AI.
Your outdated plagiarism detection systems might not be adequate to distinguish between genuine and bogus content.
In this essay, I briefly discuss this terrifying aspect of AI chatbots, examine a few techniques for online plagiarism detection, and examine how serious the situation has grown.

ChatGPT
Numerous Options For Detection
The most recent ChatGPT release from OpenAI in November 2022 catapulted chatbot expertise into the spotlight. It made it possible for the average person (or any professional) to produce intelligent, understandable essays or articles and resolve text-based mathematical issues.
The AI-created work can easily pass for a legitimate piece of writing to an uninformed or inexperienced reader, which is why students adore it, and teachers despise it.
The capacity of AI writing tools to employ natural language and grammar to create original, nearly individualized text even when the content was taken from a database, is a significant problem.
The race to defeat AI-based cheating has thus begun. Here are a few choices I discovered that are currently free.
OpenAI, the company that created ChatGPT, released the GPT-2 Output Detector to show off its chatbot text detection bot.
Users only need to enter text into a text box for Output Detector to analyze whether the text is likely to have been created by a human. The tool is simple to use.
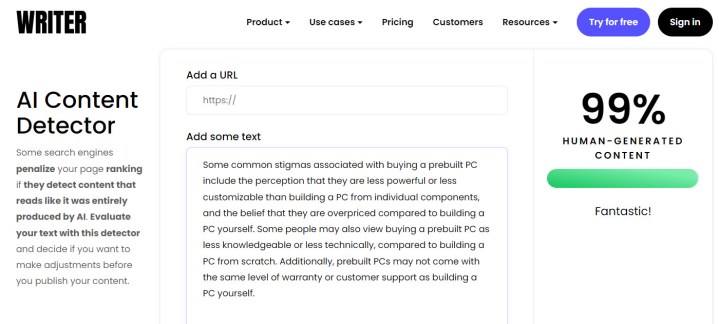
Writer AI Content Detector and Content at Scale are tools with tidy user interfaces like ZergoGPT. You can either manually input text or add a URL to scan the content (writer only).
A percentage score for the findings indicates the likelihood that humans create the content.
GPTZero is a self-made beta tool developed by Princeton University student Edward Zen and posted on Streamlit. The “algiarism” (AI-assisted plagiarism) model’s presentation of its findings sets it apart from the competition.

GPTZero
Perplexity and burstiness are the measures that GPTZero separates. Perplexity measures randomness inside a sentence, whereas burstiness assesses overall randomness across all sentences in a document.
Both measures are given numbers by the program; the lower the number, the more likely it is that a bot generated the text.
For fun, I added the Giant Language Model Test Room (GLTR), which scientists from the Harvard Natural Language Processing Group and the MIT-IBM Watson AI Lab created. Similar to GPTZero, it doesn’t clearly distinguish between “human” and “bot” in its final results.
Since bots are less likely to choose surprising terms, GLTR employs bots to detect content generated by bots. As a result, the results are displayed as a histogram with colors that compare human and AI texts.
The likelihood that the writing is from a human increase as the amount of uncertain text increases.
Making Them Undergo Testing

Demo
You might believe that given all these possibilities, AI detection is where we need to go. I wanted to use each of these technologies, though, to see how effective they were.
Therefore, I tested a few sample sentences I had written in response to queries I had also given to, in this case, ChatGPT.
My initial inquiry was straightforward: Why is purchasing a prebuilt PC frowned upon? Here are my responses and ChatGPT’s reply in comparison.
| My real writing | ChatGPT | |
| GPT-2 Output Detector | 1.18% fake | 36.57% fake |
| Writer AI | 100% human | 99% human |
| Content at Scale | 99% human | 73% human |
| GPTZero | 80 perplexity | 50 perplexity |
| GLTR | 12 of 66 words likely by human | 15 or 79 words likely by human |
As you can see, all but the first three apps could determine that my words were sincere. But ChatGPT’s response also managed to trick most of these detector apps.
For starters, it received a 99% human score on the Writer AI Content Detector app and was only identified as 36% fraudulent by the GPT-based detector.
The worst offender was GLTR, who asserted that ChatGPT’s words and mine both had an equal likelihood of being authored by humans.
But I decided to give it another go, and the reactions were much better this time. I requested from ChatGPT a synopsis of the gold particle anti-fogging study conducted at the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology.
The detector applications in this case, were far more successful in validating my own response and identifying ChatGPT.
| My real writing | ChatGPT | |
| GPT-2 Output Detector | 9.28% fake | 99.97% fake |
| Writer AI | 95% human | 2% human |
| Content at Scale | 92% human | 0% (Obviously AI) |
| GPTZero | 41 perplexity | 23 perplexity |
| GLTR | 15 of 79 words likely by human | 4 of 98 words likely by human |
In this response, the top three exams really displayed their strength. While GLTR still struggled to recognise my writing as human, at least this time, it did a fantastic job catching ChatGPT.
Conclusion
The results of each search make it clear that there are flaws in online plagiarism checkers. AI-based writing is a bit easier to spot in answers or more sophisticated writing, but it is much harder to determine in simpler answers.
But it’s not what I’d call reliable. It can be challenging for professors or editors to rely on these detecting technologies to discover cheaters when they mistakenly label some articles or essays as ChatGPT-generated.
However, they are also preparing for the advent of GPT-3, which boasts a substantially improved dataset and more advanced capabilities than GPT-2.
Developers are constantly optimizing accuracy and false positive rates (from which ChatGPT is trained).
At this stage, editors and educators will need to combine discretion and a little amount of human intuition with one (or more) of these AI detectors in order to recognize content produced by AIs.
Please refrain from using chatbots like Chatsonic, ChatGPT, Notion, or YouChat if you are a user who has or is inclined to do so in order to pass off your “job” as legitimate.
No matter how you look at it, reusing information produced by a bot (drawing on fixed sources in its database) is still plagiarism.
RELATED CTN NEWS:

Tech
US: A Judge Mandates that Google Allow Competing App Stores to Access Android

(VOR News) – The ruling is that Google, the greatest technology firm in the world, is required to make its Android smartphone operating system available to merchants that supply applications that are in direct rivalry with Google’s. This decision was reached by a judge in the United States of America.
The Android Play store, which is owned and operated by Google, was found to be an example of an illegal monopoly arrangement by a jury in the state of California on Monday. The finding was reached by a jury. Monday is the day that this decision was come to.
An earlier federal judge ruled Google’s search engine illegal.
This finding, which came after that decision, has forced the company to suffer yet another setback. As a result of the corporation having already encountered its initial obstacle, this decision has been established. This particular decision was made by the judge during the month of August, when the month was in progress.
In light of the fact that the decision was made, what exactly does it mean that the choice was accepted?
In accordance with the verdict, Google is obligated to make it possible for users to download Android app stores that are offered by third-party competitors. For a period of three years, the corporation is prohibited from imposing restrictions on the usage of payment mechanisms that are integrated into the application.
In addition, it is important to keep in mind that Google does not possess the right to impose restrictions on the utilization of ways to make payments online.
Additionally, the verdict makes it unlawful for Google to give money to manufacturers of smartphones in order to preinstall its app store. Smartphone manufacturers are prohibited from doing so.
Furthermore, it prevents Google from the possibility of sharing the revenue that is generated by the Play store with other companies that are in the industry of delivering mobile applications.
In addition to this, the court has mandated the establishment of a technical committee that will be made up of three different people chosen at random.
The committee will be responsible for monitoring the implementation of the reforms and finding solutions to any disagreements that may occur as a consequence of the implementation of the reforms while they are being implemented. This task will fall under the committee’s purview so that it may fulfill its duties.
However, certain components were allowed to be put into action until July 1st, despite the fact that the judge’s statement suggested that the ruling would take effect on November 1st. The statement was the basis for the ruling, which ultimately became effective.
Particularly, I wanted to know what Google’s reaction would be.
There is a fact that Google does not adhere to this directive, which has been brought to their attention. This document argued that the alterations that the judge had ordered to be made would “cause a range of unintended consequences that will harm American consumers, developers, and device makers.”
The judge had ordered the modifications to be implemented. The alterations were to be carried out as indicated by the judge’s ruling. The judge made it clear that he expected these revisions to be carried out in accordance with his guidance.
The company’s regulatory affairs vice president, Lee-Anne Mulholland, provided the following statement: “We look forward to continuing to make our case on appeal, and we will continue to advocate for what is best for developers, device manufacturers, and the billions of Android users around the world.”
On average, over seventy percent of the total market for smartphones and other mobile devices is comprised of mobile devices that are powered by the Android operating system. Both smartphones and other small mobile devices are included in this category.
In the event that the Play app store continues to be shown on the home page and that other Google applications are pre-installed prior to the installation of the Android application, smartphone manufacturers are entitled to install the Android application at no cost at their discretion.
Additionally, the Android application can be installed on devices that are manufactured for smartphones.
SOURCE: DWN
SEE ALSO:
Over The Planned “Link Tax” Bill, Google Threatens to Remove NZ News Links.
Tech
WhatsApp Now Features a “Mention” Tool for Status Updates and Stories.

(VOR News) – Those who use WhatsApp now have the ability to mention other people in their stories or status updates as a consequence of a feature that was only recently enabled on the platform.
Previous to this point, this capability was not available. It wasn’t until quite recently that this capability became available to the public.
According to the information that was provided by the company, users now have the opportunity to tag close friends in their stories, and the person who is mentioned will have the option to go back and re-share an earlier version of that story. This information was provided by the company. The corporation was kind enough to reveal this information to us.
Because of a new feature that has been added to the WhatsApp app, users now have the opportunity to like individual stories and status updates.
This capability was previously unavailable to WhatsApp users.
A significant amount of progress has been made in this context. Alternative readers now have the chance to “like” a work, which is comparable to liking a post on Facebook. This feature was introduced in recent years. When compared to the past, this is a tremendous shift.
At one point in time, viewers were only permitted to observe the total number of views that a particular story had gotten. These restrictions were eliminated in later versions of the software.
Additionally, it is essential that the likes and reactions to a story be kept anonymous during the entire process. One of the factors that contributes to the general mystery that surrounds this characteristic is the fact that this is one of the elements.
The person who brought it to the attention of others is the only person who will be able to judge who enjoyed it and who did not care about it. These individuals will be able to make this determination.
A notification will be issued to the individual who was referenced earlier in the sentence and who was named in the story or status update that was discussed. A notification of this nature will be sent to the individual via WhatsApp.
This message will be sent to the user in question whenever that person makes a reference to another person while they are in the process of elaborating on a narrative or updating their status. You will receive a notification alerting you that you have been tagged in the narrative.
This notification will be delivered to the person who receives this message. In addition, students will be provided with the opportunity to re-share the tale for themselves.
It is important to note that if the names of individuals who have been referenced in a narrative or a status update are included in any of these, then the names of those individuals will not be accessible to any third party through any of these. In light of the fact that the identities of those individuals will be concealed from public disclosure, this is the condition that will be required.
While WhatsApp recently made the announcement that it will be incorporating this functionality, it is highly likely that not all users will have access to it at the same time.
This is despite the fact that WhatsApp recently made this announcement.
Despite the fact that WhatsApp has only recently made a public announcement that it will move forward with the deployment, this is the situation that has presented itself.
As soon as a short period of time has elapsed, access will be made available to each and every person on the entire world.
Additionally, WhatsApp has hinted that new functionalities might be introduced to the status and updates tab in the future months.
The purpose of these capabilities is to provide users with assistance in maintaining healthy connections with the individuals who play a vital role in their living experiences. This is done in order to give users with support in maintaining close relationships with the folks who are the subject of the inquiry.
It is with the purpose of supporting users in successfully keeping close ties with the individuals in question that this step is taken.
SOURCE: DN
SEE ALSO:
Over The Planned “Link Tax” Bill, Google Threatens to Remove NZ News Links.
Accenture and NVIDIA Collaborate to Enhance AI Implementation.
Tech
Over The Planned “Link Tax” Bill, Google Threatens to Remove NZ News Links.

(VOR News) – Google has sent a strong message to the New Zealand government, threatening to stop boosting local news content should the Fair Digital News Bargaining Bill become law.
The law, put up by the Labour government and backed by the coalition in power at the moment, mandates that digital companies such as Google pay back news organizations for links to their material.
News publishers, on the other hand, charge the tech giant with “corporate bullying.”
Google says this measure may have unanticipated effects.
Google New Zealand’s country director, Caroline Rainsford, voiced her worries that the law, which is being referred to as a “link tax,” is not doing enough to support the media industry in New Zealand right now.
She underlined that Google would have to make major adjustments if the previously mentioned law were to pass, including cutting off links to news articles from its Search, News, and Discover platforms and cutting off financial ties with regional publications.
According to Rainsford, similar legislation has been proposed and approved in other nations including Australia and Canada, but it has not been proven to be effective there and breaches the principles of the open web.
She drew attention to the fact that smaller media outlets will be most negatively impacted, which will limit their capacity to reach prospective audiences.
Google says its alternative options will protect smaller, local media from negative effects.
Conversely, it conveys apprehension regarding the possible fiscal obligations and vagueness of the legislation, which it feels generates an intolerable level of ambiguity for enterprises functioning within New Zealand.
The New Zealand News Publishers Association (NPA) has reacted to Google’s warnings by alleging that the internet behemoth is using coercive tactics.
They specifically contend that the need for regulation stems from the market distortion that Google and other tech giants have created, which has fueled their expansion into some of the most significant corporations in global history.
The legislation aims to create a more equal framework that media businesses can use to negotiate commercial relationships with technological platforms that profit from their content.
New Zealand Media Editors CEO Michael Boggs stated that he was in favor of the bill, citing the fact that Google now makes a substantial profit from material created by regional publications.
He also emphasized that the use of artificial intelligence by Google—which frequently makes references to news articles without giving credit to the original sources—highlights the significance of enacting legislation.
Paul Goldsmith, the Minister of Media and Communications, has stated that the government is now evaluating various viewpoints and is still in the consultation phase.
He stated that the government and Google have been having continuous talks and will keep up these ongoing discussions.
However, not all political parties accept the validity of the Act.
The ACT Party’s leader, David Seymour, has voiced his displeasure of the proposal, saying that Google is a game the government is “playing chicken” with. He threatened the smaller media companies, saying that they would suffer from worse search engine rankings if the internet giant followed through on its promises.
Seymour contended that it is not the government’s responsibility to shield companies from shifts in the market brought about by consumer preferences.
The things that have happened in other nations are similar to what has happened in New Zealand.
Google has agreements with a number of Australian media firms that are in compliance with its News Media Bargaining Code. These agreements contain provisions that permit an annual cancellation of these agreements.
Due to the government’s decision to exempt Google from the Online News Act, the company has committed to supporting news dissemination by contributing annually to the Canadian journalistic community.
The New Zealand measure is consistent with global approaches aimed at regulating the relationships that exist between technology corporations and media organizations.
It’s hard to say what will happen with the Fair Digital News Bargaining Bill as the discussion goes on. Google and the New Zealand media landscape are preparing for what might be a protracted legal battle.
SOURCE: TET
SEE ALSO:
Accenture and NVIDIA Collaborate to Enhance AI Implementation.
-

 News3 years ago
News3 years agoLet’s Know About Ultra High Net Worth Individual
-
Entertainment2 years ago
Mabelle Prior: The Voice of Hope, Resilience, and Diversity Inspiring Generations
-

 Health3 years ago
Health3 years agoHow Much Ivermectin Should You Take?
-

 Tech2 years ago
Tech2 years agoTop Forex Brokers of 2023: Reviews and Analysis for Successful Trading
-

 Lifestyles3 years ago
Lifestyles3 years agoAries Soulmate Signs
-

 Movies2 years ago
Movies2 years agoWhat Should I Do If Disney Plus Keeps Logging Me Out of TV?
-

 Health3 years ago
Health3 years agoCan I Buy Ivermectin Without A Prescription in the USA?
-

 Learning2 years ago
Learning2 years agoVirtual Numbers: What Are They For?