Science
How Are Humanized Antibodies Made with Mouse Models?

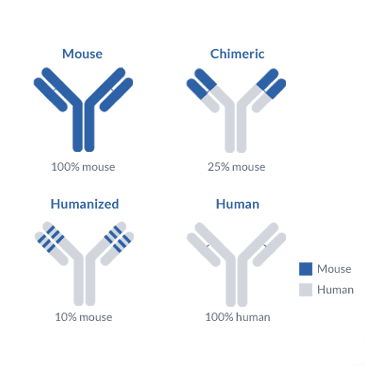
Humanized antibodies are antibodies produced in non-human animals. Humanized antibodies on production, if injected into humans, can cause damage due to variation in protein structure. These are altered earlier to become humanized.
The Necessity of Humanized Antibodies
Drugs are toxic substances and are effective when used in the appropriate dosage. However, due to the development of resistance, there is a demand for increasing dosage that is toxic to humans.
Most of the therapeutic agents are ineffective in treating various diseases.
In replacement for these therapeutic agents, antibodies are demanded. Among these antibodies, monoclonal antibodies are the best solution for passive immunity.
These humanized antibodies direly need to be produced for increasing human demands.
The Role of Mouse Models in Humanized Antibodies
Humanized antibodies are best to be generated in mouse models due to genetic similarities between humans and mice.
For example, monoclonal antibodies obtained from mice exhibit very little variation from human antibodies compared to antibodies originating from other animals.
Different Methods of Making Mouse Models
Sometimes lymphocytes of humans are fused with Epstein Barr virus or myeloma cells of the mouse to produce humanized antibodies.
But under few circumstances, the hybrid cells lose human chromosomes and become unstable. The effective ways to produce humanized antibodies are:
1. Recombinant DNA
Recombinant DNA technology is mainly used to produce humanized antibodies.
The target gene involved in antibody coding is isolated and cloned in cells, mainly mouse cells. These mouse cells will act as antibodies-producing factories.
The target gene insertion and deletion in the mouse genome required alterations to produce the desired sequence of amino acids in antibodies.
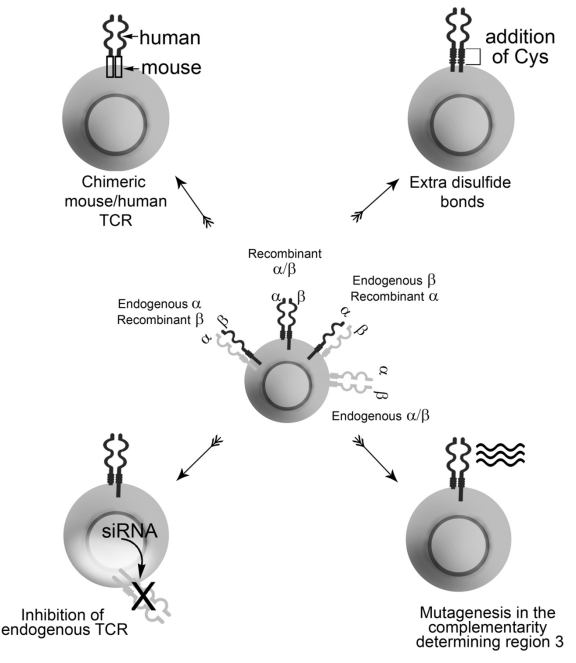
2. Chimeric Intermediate
The antibody (Fc) producing gene segment fused with the mouse antibody Fab portion to produce monoclonal antibodies in humans.
Such fusion is described as a human-mouse chimera. Mainly FC portion of the mouse antibody is replaced with the human antibody Fc portion for humanization.
The production of chimera selectively replaced the mouse antibody Fc portion with the human Fc portion. The amino acid sequences of the human Fc portion are altered by using genomic alterations tools.
In chimera, selective alterations are made in the Fab portion of the mouse that varies from the Fab portion.
The selective alterations are carried out in a way to maintain the integrity and specificity of antibodies.
The CDR region of the mouse Fab portion is never altered for selective binding of antibodies with target cells.
3. Insertion of Relevant CDRs
The recombinant DNA technology can be used to produce humanized antibodies without intervening in the chimeric intermediates.
Following the production of antibodies in the non-human system, the DNA encoding antibody may be sequenced, and the CDR region of antibodies will be determined.
Now, a strategy can be developed to produce such CDR DNA sequence-based fragments along with antibody production. The linear DNA sequences are needed for this purpose.
The Value of Humanized Antibodies Techniques
1. CDR grafting
The complementarity determining regions (CDR) are hypervariable regions of antibodies and are responsible for the specific binding of antibodies with the target.
A humanization technique is CDR grafting, in which the CDRs of parental antibodies are carefully selected and grafted into the human framework to produce humanized antibody sequences.
2. Phage Display Technologies
In phage display technology, DNA-protein, protein-protein, and peptide-peptide interactions are studied through bacteriophage.
Further, a connection is generated in a protein molecule and gene-encoded. The epitope mapping is conducted, and ligands are isolated from phage libraries.
These are useful for drug design, validation of therapeutic efficacy of drugs, and development of a vaccine.
In addition, the phage display technology is used for the strategic applications of humanized antibodies in clinical cases as therapeutic measures.
3. Transgenic Mice
The mouse-generated humanized antibodies as a therapeutic agent have been impaired due to the inherent immunogenicity of these molecules.
The production of monoclonal antibodies with very low inherent immunogenicity involves the use of transgenic mice.
The transgenic mice express repertoires for human antibody gene sequences. Transgenic mice originated humanized antibodies exhibit high specificity and efficacy compared to others.
Conclusion
Cyagen provides humanized antibodies for research and commercialization point of view and is also providing the best transgenic mice model to produce highly specific humanized antibodies.
For more information, please visit https://www.cyagen.com/us/en/.
Related CTN News:
NASA’s Dead Satellite ‘ERBS’ Returns To Earth After 38 Years

Science
NASA Switches Off Instrument On Voyager 2 Spacecraft To Save Power

NEW YORK — To save power, NASA turned off another scientific equipment on its long-running Voyager 2 spacecraft.
NASA Switches Off Instrument On the Spacecraft To Save Power
The space agency announced on Tuesday that 2’s plasma science instrument, meant to study the movement of charged atoms, was turned off in late September to allow the spacecraft to continue exploring for as long as possible, which is estimated to be into the 2030s.
NASA turned off a suite of instruments on Voyager 2 and its twin, Voyager 1, after exploring the gas giant planets in the 1980s. Both are currently in interstellar space or the region between stars. The plasma instrument on Voyager 1 stopped working years ago and was finally shut off in 2007.
The remaining four instruments on 2 will continue to collect data on magnetic fields and particles. Its mission is to investigate the regions of space beyond the sun’s protective sphere.
NASA Switches Off Instrument On Voyager 2 Spacecraft To Save Power
It launched in 1977, is the only spacecraft to have visited Uranus and Neptune. It is now more than 12 billion miles (19.31 billion kilometers) from Earth. 1 is more than 15 billion miles (24.14 billion kilometers) beyond Earth.
SOURCE | AP
Science
Hurricane Kirk Could Cause Dangerous Surf Conditions Along The US East Coast

MIAMI — Hurricane Kirk’s waves could generate life-threatening surf and rip current conditions this weekend throughout the United States East Coast, as well as in Bermuda, the Greater Antilles, and the Bahamas, according to forecasters.
Kirk was a Category 3 hurricane in the middle Atlantic Ocean that might grow further but was predicted to stay away from land, according to the Miami-based National Hurricane Center on Thursday.
Hurricane Kirk Could Cause Dangerous Surf Conditions Along The US East Coast
Kirk-generated swells were forecast to reach parts of the Leeward Islands on Friday, Bermuda and the Greater Antilles on Saturday, and the East Coast and the Bahamas on Sunday, according to the center.
No coastal watches or warnings were in effect. The major storm was around 1,130 miles (1,820 kilometers) east of the Leeward Islands, with maximum sustained winds of 125 mph (205 km/h).
Meanwhile, Tropical Storm Leslie formed late Wednesday in the eastern Atlantic and is expected to strengthen into a hurricane in the following days, forecasters said. It was also not considered a threat to the land.
Hurricane Kirk Could Cause Dangerous Surf Conditions Along The US East Coast
The storm was about 540 miles (870 kilometers) southwest of Cabo Verde’s southernmost tip, with maximum sustained winds of 45 mph (75 kph), according to the center.
The storms raged in the Atlantic as rescuers in the United States Southeast sought for missing persons after Hurricane Helene struck last week, leaving a trail of death and devastation.
SOURCE | AP
Science
NASA Sends First Manned Starliner Spacecraft to Space Station

NASA has announced astronauts Butch Wilmore and Suni Williams are safely in orbit on the first crewed flight test of Boeing’s Starliner spacecraft heading for the International Space Station.
As part of NASA’s Boeing Crew Flight Test, the astronauts launched a ULA (United Launch Alliance) Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex-41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida at 10:52 a.m. EDT Wednesday for an end-to-end test of the Starliner system.
“Two brave NASA astronauts are well on their way to this historic first test flight of a brand-new spacecraft,” stated NASA Administrator Bill Nelson. “Boeing’s Starliner represents a new era of American exploration. Human spaceflight is a risky endeavor, but it is worth it. It is an exciting time for NASA, our commercial partners, and the future of space exploration. “Go Starliner, Butch, and Suni!”
The flight test is part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program and will help validate the transportation system, launch pad, rocket, spacecraft, in-orbit operations capabilities, and return to Earth with astronauts aboard as the agency prepares to certify Starliner for rotational missions to the space station. Starliner has already completed two uncrewed orbital missions, including a test to and from the space station, as well as a pad abort demonstration.

Boeing Starliner Makes Orbit
“With Starliner’s launch, separation from the rocket, and arrival in orbit, Boeing’s Crew Flight Test is right on track,” said Mark Nappi, vice president and program manager for Boeing’s Commercial Crew Program. “Everyone is focused on giving Suni and Butch a safe, comfortable, ride and performing a successful test mission from start to finish.”
Boeing’s mission control center in Houston will supervise a sequence of autonomous spacecraft maneuvers while Starliner is in flight. NASA teams will supervise space station activities from the Mission Control Center at the agency’s Johnson Space Center in Houston.
“Flying crew on Starliner represents over a decade of work by the Commercial Crew Program and our partners at Boeing and ULA,” said Steve Stich, Commercial Crew Program Manager at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston. “For many of us, this is a career-defining occasion, ushering in a new crew transportation capacity for our agency and our country. We will take it one step at a time, putting Starliner through its paces and remaining watchful until Butch and Suni safely land back on Earth at the end of this test journey.”
At about 12:15 p.m., Starliner will dock autonomously to the forward-facing port of the station’s Harmony module. Thursday, June 6, and will remain at the orbital laboratory for almost a week.
Wilmore and Williams will help ensure that the spacecraft is functioning properly by testing the environmental control system, the displays and control system, and moving the thrusters, among other things, during flight.
Wilmore and Williams will join the Expedition 71 crew, which includes NASA astronauts Michael Barratt, Matt Dominick, Tracy C. Dyson, and Jeanette Epps, as well as Roscosmos cosmonauts Nikolai Chub, Alexander Grebenkin, and Oleg Kononenko.
NASA’s arrival and in-flight event coverage is as follows (all times Eastern and subject to change depending on real-time operations):
NASA Television channels will continue to broadcast the Starliner’s mission.
Thursday, June 6
9:30 a.m. – Arrival coverage begins on NASA+, the NASA app, and YouTube, and continues on NASA Television and the agency’s website.
12:15 p.m. – Targeted docking
2 p.m. – Hatch opening
2:20 p.m. – Welcome remarks
3:30 p.m. – Post-docking news conference at NASA Johnson with the following participants:
- NASA Associate Administrator Jim Free
- Steve Stich, manager, NASA’s Commercial Crew Program
- Jeff Arend, manager for systems engineering and integration, NASA’s International Space Station Office
- Mark Nappi, vice president and program manager, Commercial Crew Program, Boeing
Coverage of the post-docking news conference will air live on NASA+, NASA Television, the NASA app, YouTube, and the agency’s website.
To attend the post-docking briefing, U.S. media must contact the NASA Johnson newsroom at: [email protected] or 281-483-5111 by 1 p.m. Thursday, June 6. To join by phone, media must contact the NASA Johnson newsroom by 3 p.m. Thursday, June 6.
5:50 p.m. – NASA Administrator Bill Nelson, Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy, Associate Administrator Jim Free, Associate Administrator for Space Operations Ken Bowersox, and Johnson Space Center Director Vanessa Wyche will speak with Wilmore and Williams about their launch aboard the Starliner spacecraft.
Coverage of the Earth to space call will air live on NASA+, NASA Television, the NASA app, YouTube, and the agency’s website.
Saturday, June 8
8:50 a.m. – NASA astronauts Wilmore and Williams will provide a tour of Starliner.
Coverage of the in-orbit event will stream live on NASA+, NASA Television, the NASA app, YouTube, and the agency’s website.
Monday, June 10
11 a.m. – Williams will speak to students from Sunita L. Williams Elementary School in Needham, Massachusetts, in an event aboard the space station.
Coverage of the Earth to space call will air live on NASA+, NASA Television, the NASA app, YouTube, and the agency’s website.
Tuesday, June 11
3:15 p.m. – Wilmore will speak to students from Tennessee Tech University in an event aboard the space station.
Coverage of the Earth to space call will air live on NASA+, NASA Television, the NASA app, YouTube, and the agency’s website.
-

 News3 years ago
News3 years agoLet’s Know About Ultra High Net Worth Individual
-
Entertainment2 years ago
Mabelle Prior: The Voice of Hope, Resilience, and Diversity Inspiring Generations
-

 Health4 years ago
Health4 years agoHow Much Ivermectin Should You Take?
-

 Tech2 years ago
Tech2 years agoTop Forex Brokers of 2023: Reviews and Analysis for Successful Trading
-

 Lifestyles3 years ago
Lifestyles3 years agoAries Soulmate Signs
-

 Movies2 years ago
Movies2 years agoWhat Should I Do If Disney Plus Keeps Logging Me Out of TV?
-

 Health3 years ago
Health3 years agoCan I Buy Ivermectin Without A Prescription in the USA?
-

 Learning3 years ago
Learning3 years agoVirtual Numbers: What Are They For?
